The divide between art and science, often portrayed as a dichotomy, is increasingly being blurred as artists find inspiration in scientific concepts, and scientists acknowledge the creative processes inherent in their work. This convergence of disciplines not only challenges traditional boundaries but also opens up new avenues for exploration and understanding. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world where art and science intersect, examining how artists draw inspiration from scientific concepts and how this fusion enriches both fields.
Inform and Enrich each other
Art and science, seemingly disparate fields, possess unique strengths and perspectives that can mutually benefit and enhance each other. Here are several ways in which art and science can inform and enrich one another:
- Inspiration and Creativity: Art has the power to inspire scientific inquiry by depicting complex ideas visually and evoking curiosity. Similarly, scientific discoveries can serve as a wellspring of inspiration for artists, sparking creative exploration of new concepts and perspectives.
- Communication and Visualization: Artistic techniques can be employed to communicate scientific concepts in a visually compelling and accessible manner. Scientific visualization, in turn, can enhance artistic representations by providing accurate and informative depictions of natural phenomena. Leading to a deeper understanding and appreciation of both disciplines.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Collaboration between artists and scientists can foster innovative approaches to problem-solving and research. By bringing together diverse perspectives and skill sets, interdisciplinary teams can tackle complex challenges from multiple angles, leading to novel insights and discoveries.
- Humanizing Science and Technology: Art can humanize scientific and technological advancements by exploring their social, ethical, and cultural implications. Through storytelling, visual art, and performance, artists can engage audiences in critical dialogue about the impact of science and technology on society, fostering greater awareness and empathy.
- Aesthetic Exploration and Design: Artistic principles can inform the design and aesthetics of scientific instruments, experiments, and technologies, enhancing their functionality and user experience. Conversely, scientific principles such as symmetry, proportion, and harmony can inspire artistic expression and aesthetic innovation.
- Emotional Engagement and Empathy: Art has the ability to evoke emotional responses and foster empathy, enriching our understanding of scientific concepts and their real-world implications. By connecting on an emotional level, art can engage a broader audience and encourage greater public interest and support for scientific research and education.
- Cultural Reflection and Critique: Artistic exploration of scientific themes can provide a platform for cultural reflection and critique, challenging societal norms and assumptions about science, technology, and progress. Through satire, parody, and irony, artists can prompt viewers to question existing power structures and paradigms. Fostering a more nuanced understanding of science and its role in society.
- Cross-Pollination of Ideas: The exchange of ideas between art and science can lead to unexpected discoveries and innovations. By embracing curiosity and openness to new perspectives. Artists and scientists can learn from each other and push the boundaries of their respective disciplines, enriching both fields in the process.
Overall, the intersection of art and science offers endless opportunities for mutual enrichment and collaboration, highlighting the interconnectedness of human creativity, curiosity, and exploration. Additionally, by embracing interdisciplinary approaches and fostering dialogue between artists and scientists, we can unlock new insights, inspire innovation, and deepen our understanding of the world around us.
Bridging Two Worlds

Historically, art and science have been perceived as distinct domains, with art emphasizing creativity and expression, and science focusing on empirical evidence and rationality. However, this simplistic view overlooks the inherent connections between the two. Both disciplines involve observation, experimentation, and interpretation. Artists and scientists alike seek to make sense of the world around them, albeit through different lenses.
Artistic Exploration of Scientific Concepts
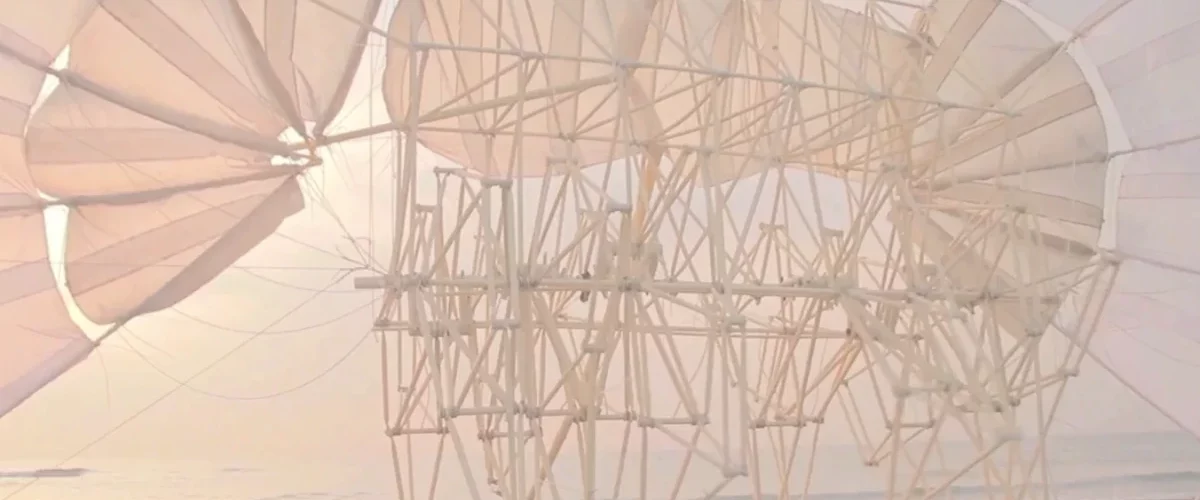
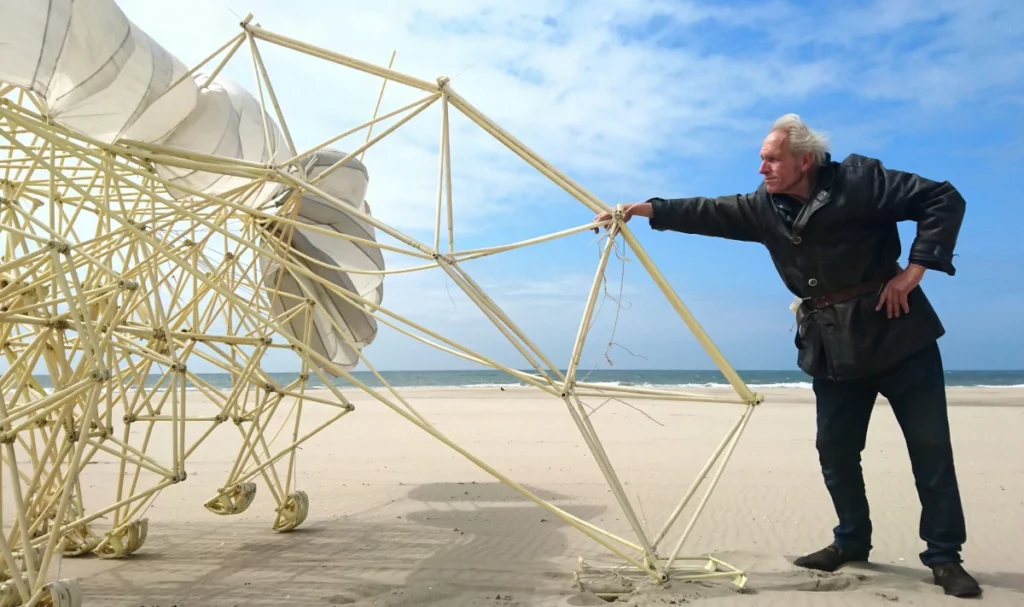
In recent years, artists have increasingly turned to science for inspiration, finding beauty in the complexity of natural phenomena and the elegance of scientific theories. One prominent example is the work of Dutch artist Theo Jansen. Who creates kinetic sculptures known as “Strandbeests” inspired by the principles of biology and engineering. These mesmerizing creations mimic the movements of living organisms and challenge our perceptions of art and technology.
Similarly, the field of bioart has emerged at the intersection of biology and art, with artists using living organisms as their medium to explore themes. Such as genetic engineering, biotechnology, and the relationship between humans and nature. Artists like Eduardo Kac have famously created transgenic artworks. Incorporating genetic material from different species to provoke thought and dialogue about ethical and social issues surrounding biotechnology.
Science as a Source of Inspiration
While artists find inspiration in scientific concepts, scientists also recognize the value of creativity in their work. The process of scientific discovery often involves imagination, intuition, and unconventional thinking. For example, Nobel laureate physicist Richard Feynman famously emphasized the importance of creativity in scientific inquiry, stating, “Science is imagination in the service of the verifiable truth.”
Moreover, scientific visualization plays a crucial role in communicating complex ideas to a broader audience. Scientists employ artistic techniques to represent data and phenomena visually, allowing for greater comprehension and appreciation of scientific concepts. From elegant mathematical equations to intricate computer-generated simulations. These visualizations not only aid in scientific research but also serve as sources of inspiration for artists.
Enriching Both Fields
The fusion of art and science offers numerous benefits to both disciplines. Moreover, for artists, exploring scientific concepts provides a deeper understanding of the natural world and expands the possibilities for creative expression. By integrating scientific principles into their work, artists can communicate complex ideas in engaging and accessible ways. Fostering interdisciplinary dialogue and collaboration.
Likewise, for scientists, engaging with art can lead to new insights and perspectives. Artistic representations of scientific concepts can spark curiosity and inspire further exploration, leading to breakthroughs in research and innovation. Additionally, collaborations between artists and scientists can facilitate interdisciplinary approaches to problem-solving, leading to novel solutions and discoveries.
Conclusion
However, the intersection of art and science represents a rich and fertile ground for exploration and creativity. By breaking down traditional barriers and embracing interdisciplinary collaboration. Artists and scientists can enrich each other’s work and foster a deeper understanding of the world around us. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the 21st century. The fusion of art and science offers boundless opportunities for discovery, innovation, and inspiration.
